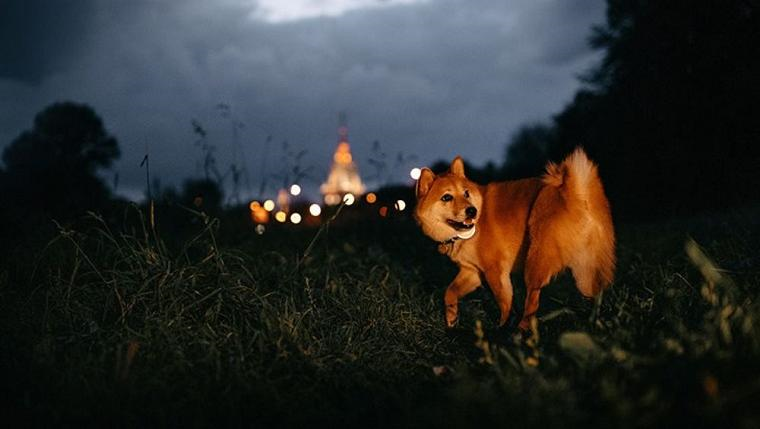



As pet owners, we often wonder how well our furry companions see at night. Have you ever noticed your dog moving confidently in a pitch-dark room or navigating outdoor spaces without hesitation? This raises the question: Can dogs see in the dark? In this article, we’ll explore how dogs perceive darkness, how their night vision compares to humans and other animals, and whether they need a light on at night.
Do Dogs Have Night Vision?
Yes, dogs have enhanced night vision compared to humans. While they cannot see in total darkness the way some nocturnal animals can, their eyes are specially adapted to help them see better in low-light conditions.
Dogs have a structure in their eyes called the tapetum lucidum, a reflective layer behind the retina that enhances night vision by bouncing light back through the retina. This allows them to capture and utilize available light more efficiently, making it easier for them to see in dim environments.
Additionally, dogs have more rod cells in their retinas than humans. Rod cells are responsible for detecting light and motion, which helps dogs see shapes and movements more clearly at night, even when details might be hard to distinguish.
Do Dogs See Better Than Humans at Night?
Yes! Dogs have significantly better night vision than humans. Here's why:
• More Rod Cells – Rod cells detect light, and dogs have more of them, making them more sensitive to dim light.
• Tapetum Lucidum – This reflective layer acts like a mirror, amplifying available light and helping dogs see in low-light conditions.
• Wider Pupils – Dogs’ pupils can open wider than human pupils, allowing more light to enter their eyes.
While humans rely heavily on color perception and detail, dogs prioritize movement and contrast, which helps them detect objects even in near darkness. However, in complete darkness (such as a windowless room with no light source), dogs will struggle to see, just like humans.
Do Dogs Need a Light on at Night?
Most dogs do not need a light on at night. Their eyes adjust well to low-light conditions, and they can navigate using their superior sense of smell and hearing. However, there are exceptions:
• Senior Dogs: Older dogs may develop vision problems like cataracts or night blindness. In such cases, keeping a dim nightlight on can help them navigate.
• Anxious Dogs: Some dogs feel more comfortable with a small light source, especially if they experience separation anxiety at night.
• New Environments: If your dog is in an unfamiliar place, a nightlight can prevent them from bumping into furniture or feeling disoriented.
For most dogs, however, leaving a light on is unnecessary, as they can navigate using their heightened senses.
Can Dogs See Better Than Cats at Night?
While dogs have impressive night vision, cats see even better in the dark. Here's why:
• Cats have an even more advanced tapetum lucidum, reflecting more light than a dog's.
• Cats have even more rod cells than dogs, making them superior in low-light environments.
• Cats’ eyes can dilate more, allowing maximum light intake.
Although dogs can navigate well in dim lighting, they are not as efficient as cats, who are true nocturnal hunters.
Can Dogs See Glow-in-the-Dark Objects?
Yes, dogs can see glow-in-the-dark objects, but not in the same way humans do.
• Glow-in-the-dark toys work by absorbing light and then slowly releasing it as a glow. Since dogs see well in dim light, they can detect the glowing object, but they might not see it as vividly as we do.
• Dogs see fewer colors than humans. While humans see a full spectrum of colors, dogs mostly see shades of blue and yellow. If a glow-in-the-dark object falls within this spectrum, it will be more visible to them.
If you want your dog to enjoy glow-in-the-dark toys, ensure they are exposed to light before playtime so they are properly charged.
Final Thoughts
Dogs do not have perfect night vision, but they can see much better than humans in dim lighting. Their tapetum lucidum, wider pupils, and increased rod cells give them an advantage in darkness. While they don't see as well as cats at night, they navigate efficiently in low-light conditions.
Most dogs don't need a nightlight, but older or anxious dogs might benefit from one. If you're playing with your dog in the dark, glow-in-the-dark toys can be a fun option—just keep in mind that they may not appear as vibrant to dogs as they do to humans.
2018-2025 © Uhappyzone.All Rights Reserved.